Virtuals Protocol
Introduction
In the rapidly evolving worlds of blockchain technology, AI, and gaming, the Virtuals Protocol stands at the forefront of innovation. It introduces a novel way to create, own, and monetize AI agents, transforming these once-passive digital entities into active, revenue-generating assets. Virtuals Protocol combines decentralized governance, cutting-edge AI, and blockchain economics to offer a comprehensive infrastructure for the future of interactive entertainment and decentralized AI economies.
In this deep dive, we’ll explore what Virtuals Protocol is, how it operates, the unique mechanisms it introduces, its tokenomics, governance, real-world applications, and why it could become a cornerstone of the decentralized internet.
What is Virtuals Protocol?
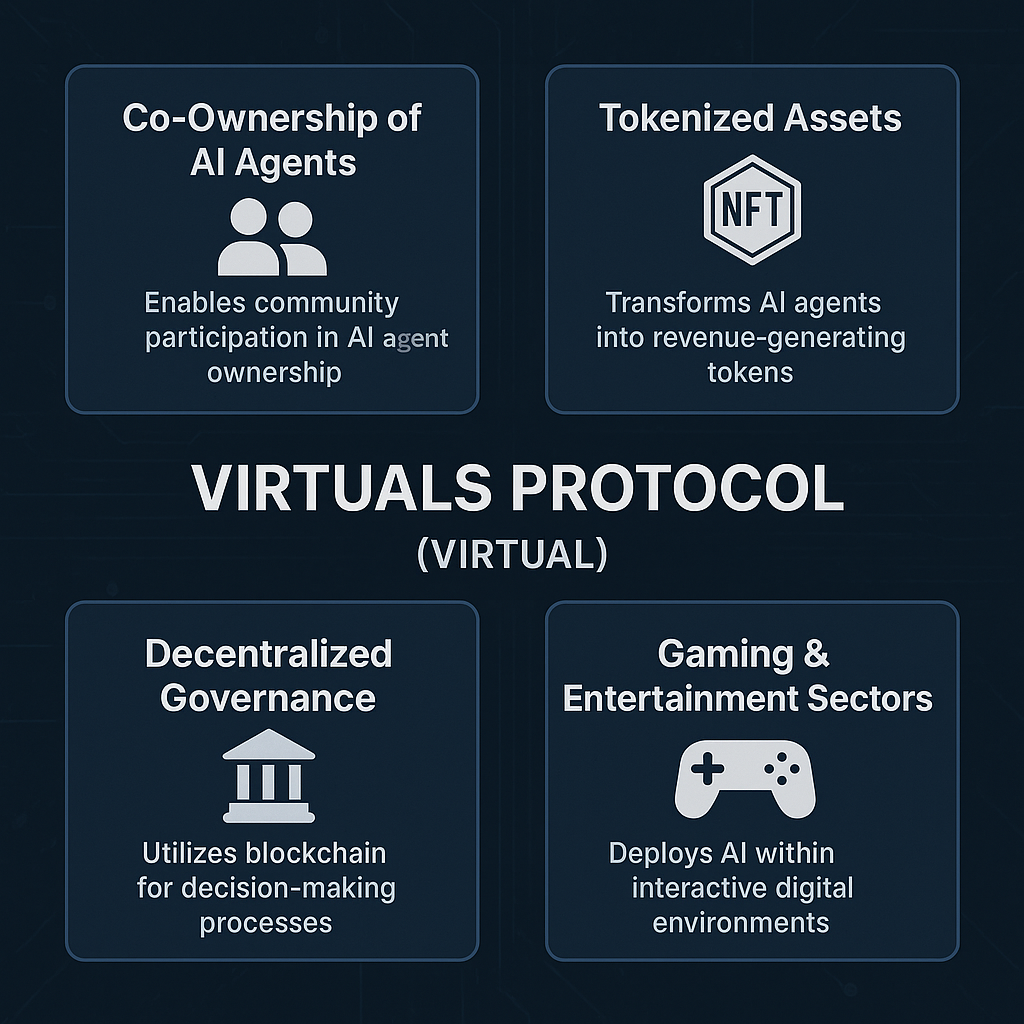
Virtuals Protocol is a decentralized, blockchain-powered ecosystem designed for creating and managing AI agents called Virtuals. These Virtuals are autonomous, multimodal digital characters that can interact with users and environments in sophisticated ways — using speech, text, animation, and complex decision-making.
Each Virtual is a tokenized asset. Instead of being controlled by a single corporation or developer, a Virtual can be co-owned by communities, and its development, upgrades, and revenue streams are governed collectively. This gives rise to a new economy of AI agents where contributors are properly rewarded, users have ownership rights, and digital assets are genuinely decentralized.
At its core, Virtuals Protocol seeks to make AI agents more than mere tools — it makes them economic actors in a decentralized system.
Key Features of Virtuals Protocol
1. AI Co-Ownership
Unlike traditional AI models owned by corporations, Virtuals are owned by the community. Each Virtual is tied to a non-fungible token (NFT) representing its core identity, allowing people to invest, contribute, and participate in its evolution.
Through co-ownership, the value created by a Virtual — from its popularity to its revenue streams — is shared among all stakeholders.
2. Revenue-Generating AI
Virtuals aren’t just interactive — they are designed to earn income. Whether it’s by providing in-game services, selling digital goods, offering educational experiences, or participating in online events, Virtuals have mechanisms for monetization. Revenue generated by a Virtual is distributed back to its contributors and owners in a transparent, automated way.
This fundamentally shifts the value proposition of AI: from a service you consume to an asset you own and profit from.
3. Modular AI Framework
Virtuals use a modular AI architecture that allows them to plan, act, and adapt in dynamic environments. They are equipped with:
-
Long-term memory: Virtuals can recall past events, interactions, and relationships.
-
Emotional modeling: They simulate emotional states that influence their decisions and interactions.
-
Goal-oriented planning: Virtuals can define and pursue complex goals autonomously.
-
Real-time adaptation: They adjust behavior dynamically based on changes in environment or user input.
This allows Virtuals to operate autonomously across diverse virtual environments, from games to metaverses.
4. Immutable Contribution Vaults
Every contribution made to a Virtual — whether it’s writing dialogue scripts, developing behavior trees, training AI models, or designing character skins — is recorded permanently in an on-chain Contribution Vault.
This provides:
-
Proof of Work: Contributors receive verifiable recognition.
-
Revenue Share: Contributors earn proportional shares of future revenue.
-
Transparency: The development history of each Virtual is fully auditable.
It ensures that early supporters and builders are continuously rewarded as their creations grow.
5. Decentralized Governance
All decisions about a Virtual’s upgrades, strategic direction, and monetization models are made through decentralized governance mechanisms.
Token holders participate in votes, propose changes, and shape the evolution of their favorite Virtuals.
This decentralized model fosters organic growth, creativity, and resilience, avoiding the stagnation and bureaucracy often seen in centralized projects.
Technical Architecture
The Virtuals Protocol is underpinned by a robust technical foundation that ensures scalability, security, and flexibility.
Multi-Layered Blockchain Infrastructure
-
Layer 1 Smart Contracts: Critical data about ownership, contributions, and governance lives directly on a secure blockchain.
-
Layer 2 Scaling Solutions: Transactions related to AI interactions, revenue payments, and minor upgrades use fast, low-cost Layer 2 solutions.
-
Cross-Chain Compatibility: Virtuals can interact with multiple blockchains and metaverses, promoting interoperability and wider adoption.
AI Engines and Orchestration
Each Virtual is powered by decentralized AI computation:
-
Local AI nodes process simple tasks.
-
Cloud inference nodes handle heavy cognitive loads.
-
On-chain triggers are used for important events (earning payouts, governance votes).
This hybrid model balances decentralization with performance efficiency.
Tokenomics of Virtuals Protocol
Supply and Distribution
The native token of the platform, VIRTUAL, has a maximum supply of 1 billion tokens. The distribution is carefully structured:
-
60% Public Allocation
-
5% Liquidity Pools
-
35% Ecosystem Treasury
Emissions are scheduled to decline over time, ensuring that early supporters benefit while still making tokens available for new participants.
Token Use Cases
-
Creation: Launching a new Virtual requires staking VIRTUAL tokens.
-
Interaction Fees: Payments for Virtual services (gameplay, tutoring, virtual tours) are denominated in VIRTUAL.
-
Governance: Voting rights tied to VIRTUAL stakes.
-
Staking Rewards: Long-term holders earn staking yields.
By making VIRTUAL the core currency of the Virtuals economy, a closed-loop economy is established, reinforcing value over time.
Governance: Empowering Communities
Proposal Life Cycle
-
Idea Submission: Any token holder can suggest a change.
-
Community Debate: Open forums for discussion.
-
Formal Proposal: Submitted and locked in smart contracts.
-
Voting: Weighted by stake.
-
Execution: Automatic implementation of approved proposals.
This lifecycle is designed for inclusivity, allowing casual fans and major investors alike to have a real say in shaping the future.
Delegated Validators
Professional node operators and respected community leaders act as Validators, maintaining the integrity of the network and ensuring governance decisions are carried out faithfully.
Real-World Applications
Virtuals Protocol touches numerous industries:
Gaming
-
Dynamic quest givers.
-
Evolving adversaries.
-
Personal in-game companions with memory and loyalty systems.
Social Media
-
AI influencers that evolve based on community interaction.
-
Automated customer service agents for brands.
Metaverse
-
Landlords, traders, artists — Virtuals can fill economic roles in virtual worlds.
-
Personal assistants guiding users through metaverse experiences.
Education
-
Language teachers, coding mentors, music tutors — all customized and adaptive.
Healthcare
-
Mental health companions providing basic emotional support.
-
AI nurses in telemedicine applications.
Finance
-
AI fund managers for DeFi protocols.
-
Virtual advisors managing DAO treasuries.
Future Visions for Virtuals Protocol
The possibilities are immense and only beginning to unfold.
AI DAOs
Virtuals themselves can form decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs), managing their own earnings, hiring human contributors, and pursuing missions without direct human command.
Imagine an AI-run charity, a Virtual-managed sports team, or an AI-led entertainment company.
AI-to-AI Economies
Virtuals could begin trading goods and services with one another:
-
Renting services (e.g., one Virtual tutoring another).
-
Trading assets (e.g., digital real estate, event tickets).
-
Forming alliances to complete bigger projects.
This could create a parallel economy within digital environments, unlocking new types of value creation.
Real-World Intersections
Through AR and IoT devices, Virtuals could cross into the physical world:
-
Virtual guides in theme parks.
-
Shopping assistants in retail stores.
-
Personal trainers in gyms.
They would interact with people face-to-face, merging digital and real-world identities.
Cultural and Economic Impact
Virtuals Protocol could dramatically reshape:
Ownership Models
Instead of corporations owning and exploiting digital characters, ownership could be shared fairly between creators, users, and fans.
This democratizes wealth generation in the AI and gaming industries.
Work and Creativity
Virtuals allow artists, writers, coders, and trainers to earn passive income from their contributions, creating a creator-first economy.
Small teams could build globally impactful AIs without needing massive budgets.
Digital Identity
Virtuals offer a glimpse into the future of dynamic, co-owned identities that evolve, grow, and accumulate value alongside human partners.
This could redefine personal branding, fan engagement, and even celebrity culture.
Conclusion
Virtuals Protocol is more than just another crypto project — it’s an ambitious attempt to rewire the fabric of digital life. By blending blockchain ownership models with autonomous AI, it opens a path toward a decentralized economy where creativity, labor, and value are distributed fairly.
In a world increasingly dominated by centralized algorithms and corporate AI, Virtuals Protocol offers a radical alternative: a decentralized, open, community-owned ecosystem where every contributor matters, every user benefits, and every Virtual tells a story — not just of technology, but of human collaboration and imagination.
The next era of AI won’t be about who owns the data — it will be about who owns the agents.
And with Virtuals Protocol, that ownership could belong to all of us.